Sleeve Gastrectomy Surgery — A Solution for Morbid Obesity?
Introduction: A Solution for Morbid Obesity
A Solution for Morbid Obesity: Morbid obesity is a severe health condition that significantly increases the risk of various chronic diseases and can dramatically reduce life expectancy. Traditional weight loss methods often prove insufficient for individuals with morbid obesity, making surgical interventions a necessary consideration. Sleeve gastrectomy, a popular bariatric surgery, offers a promising solution. This article explores the mechanics, benefits, risks, and overall effectiveness of sleeve gastrectomy as a treatment for morbid obesity.
Understanding Morbid Obesity
Definition and Health Implications
A Solution for Morbid Obesity: Morbid obesity is typically defined as having a Body Mass Index (BMI) of 40 or higher, or a BMI of 35 or higher with associated health conditions such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, or sleep apnea. This condition poses significant health risks, including:
- Cardiovascular Disease: Increased risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Higher likelihood of developing insulin resistance and diabetes.
- Joint Problems: Excess weight places additional stress on joints, leading to conditions like osteoarthritis.
- Sleep Apnea: Obesity can cause obstructive sleep apnea, leading to poor sleep quality and increased cardiovascular risk.
- Reduced Life Expectancy: Morbid obesity can shorten life expectancy by up to 20 years.
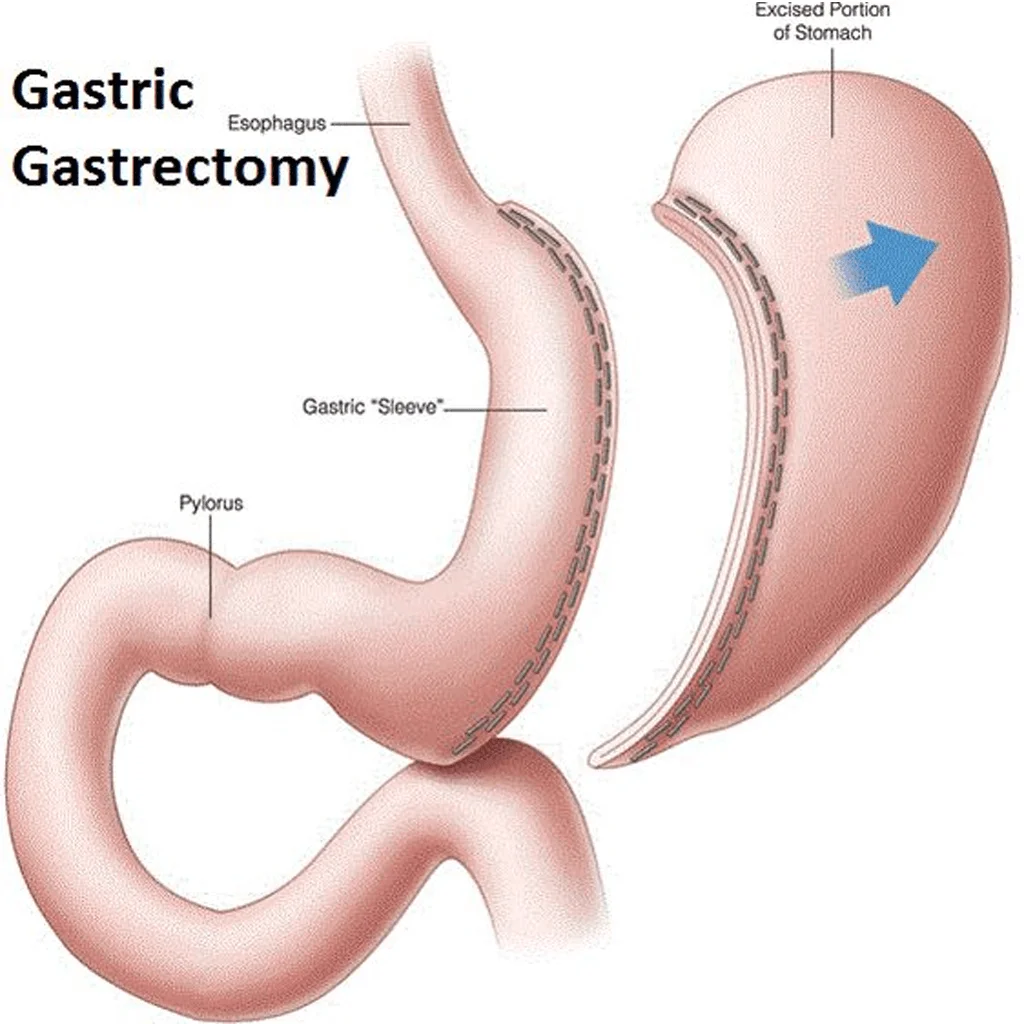
What is Sleeve Gastrectomy?
A Solution for Morbid Obesity: Procedure Overview
Sleeve gastrectomy, also known as gastric sleeve surgery, involves the removal of approximately 75-80% of the stomach. This results in a tube-like structure or “sleeve” that limits the amount of food the stomach can hold, thereby reducing calorie intake. The procedure is performed laparoscopically, meaning it involves small incisions and the use of a camera to guide the surgery.
Mechanism of Action
The primary mechanisms through which sleeve gastrectomy promotes weight loss include:
- Restriction: The reduced stomach size limits food intake.
- Hormonal Changes: Removal of the stomach portion that produces ghrelin, the hunger hormone, helps decrease appetite.
A Solution for Morbid Obesity: Benefits of Sleeve Gastrectomy
1. Significant Weight Loss
Patients typically lose 50-70% of their excess weight within the first year post-surgery. This substantial weight loss can significantly improve overall health and quality of life.
2. Improvement in Obesity-Related Conditions
Sleeve gastrectomy can lead to the improvement or resolution of many obesity-related conditions, including:
- Type 2 Diabetes: Many patients experience remission of diabetes.
- Hypertension: Blood pressure levels often decrease, reducing the need for medication.
- Sleep Apnea: Weight loss can alleviate symptoms of sleep apnea, leading to better sleep quality.
- Joint Pain: Reduced weight load on joints can decrease pain and improve mobility.
3. Enhanced Quality of Life
Weight loss and improved health conditions often result in increased physical activity, higher self-esteem, and better mental health. Patients report a higher quality of life post-surgery, with more participation in social and recreational activities.
4. Minimally Invasive Approach
The laparoscopic technique used in sleeve gastrectomy means smaller incisions, less postoperative pain, and faster recovery times compared to traditional open surgery.
A Solution for Morbid Obesity: Risks and Considerations
1. Surgical Risks
As with any surgery, sleeve gastrectomy carries inherent risks, including:
- Infection: Postoperative infections can occur at the incision sites or internally.
- Bleeding: There is a risk of bleeding during and after the surgery.
- Adverse Reactions to Anesthesia: Complications related to anesthesia can occur, including allergic reactions and respiratory issues.
- Blood Clots: There is a risk of developing blood clots in the legs (deep vein thrombosis) that can travel to the lungs (pulmonary embolism).
2. Postoperative Complications
Specific complications can arise after the surgery, including:
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Reduced food intake and absorption can lead to deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals, such as iron, calcium, vitamin B12, and folate.
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Some patients may develop or experience worsening of acid reflux.
- Strictures: Narrowing of the stomach sleeve can occur, leading to difficulty in food passage.
3. Long-Term Considerations
- Lifestyle Changes: Successful outcomes depend on a patient’s willingness to commit to significant lifestyle changes, including diet modifications, regular exercise, and adherence to medical follow-up.
- Psychological Impact: The psychological effects of rapid weight loss and body image changes can be challenging. Some patients may experience depression or anxiety.
- Potential for Weight Regain: Although less common than with traditional weight loss methods, some patients may experience weight regain if they do not adhere to recommended lifestyle changes.
A Solution for Morbid Obesity: The Process of Undergoing Sleeve Gastrectomy
Preoperative Evaluation
A thorough preoperative evaluation is necessary to determine suitability for surgery. This includes:
- Medical History Review: Assessing the patient’s medical history and any pre-existing conditions.
- Physical Examination: Conducting a comprehensive physical examination.
- Nutritional and Psychological Assessments: Evaluating the patient’s nutritional status and mental readiness for the surgery.
- Diagnostic Tests: Performing blood tests, imaging studies, and other necessary diagnostic procedures.
The Surgery
On the day of the surgery, patients are admitted to the hospital. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia and typically lasts 1–2 hours. After surgery, patients are monitored in the recovery room before being transferred to their hospital room.
Postoperative Care
Patients usually stay in the hospital for a few days post-surgery. During this time, they receive pain management, hydration, and nutritional support. The postoperative diet progresses gradually from liquids to pureed foods, and eventually to solid foods over several weeks. Lifelong nutritional supplements and regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor progress and prevent deficiencies.
A Solution for Morbid Obesity: Long-Term Success and Maintenance
Diet and Nutrition
Maintaining a balanced, nutrient-rich diet is crucial for long-term success. Patients must follow dietary guidelines provided by their healthcare team to ensure adequate nutrient intake and prevent deficiencies. This often includes a focus on high-protein foods, vitamins, and minerals.
Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is important for maintaining weight loss and overall health. Patients are encouraged to increase their activity levels gradually, starting with gentle exercises such as walking and progressing to more vigorous activities as they recover. Physical activity not only aids in weight loss but also enhances cardiovascular health and overall fitness.
Psychological Support
The psychological aspect of weight loss is significant. Many patients benefit from counseling or support groups to help them adjust to their new lifestyle and cope with any emotional challenges. Mental health support can address issues related to body image, self-esteem, and the psychological impact of significant weight loss.
Conclusion: A Solution for Morbid Obesity
A Solution for Morbid Obesity: Gastric Sleeve is a highly effective solution for individuals struggling with morbid obesity, offering significant weight loss and improvement in obesity-related health conditions. While it comes with risks and requires a strong commitment to lifestyle changes and ongoing medical supervision, the benefits often outweigh the challenges.
A Solution for Morbid Obesity
For those considering sleeve gastrectomy, consulting experienced bariatric surgeons and undergoing a thorough evaluation can help determine the best approach for achieving long-term success and improved quality of life.